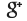The Liberty engine was America's most important contribution to aeronautical technology during World War I. Jesse G. Vincent of Packard and Elbert J. Hall of Hall-Scott co-designed it in mid-1917 for the US government, which wanted a standard design in 4-, 6-, 8-, and 12-cylinder versions that could be quickly mass-produced to equip US combat aircraft. Automakers Ford, Lincoln, Packard, Marmon, and Buick produced 20,748 Liberty 12s before the Armistice, which insured their widespread use into the 1920s and '30s. This is one of the four Ford Motor Co. Liberty 12 Model A's that powered the Navy-Curtiss NC-4, the first aircraft to cross the Atlantic Ocean, May 16-31, 1919. The Model A also powered such aircraft as the Fokker T2, and the Douglas World Cruiser.